We use our hands extensively for many simple yet essential tasks like – eating, maintaining hygiene, carrying. An injury or condition that affects one or both of our hands usually turn these routine tasks into big challenges.
Dr Gautam Tawari is one of best trained Orthopedic hand surgeons in Mumbai, India. He has trained at the Pulvertaft Hand Centre (UK) which is an apex institute for Hand surgery training in the United Kingdom and the world.
Orthopedic Hand surgery is about restoration of hand function, Dr Tawari offers a comprehensive evaluation, diagnosis and treatment of both simple and complex conditions of the hand, thumb, fingers, wrist and forearm.
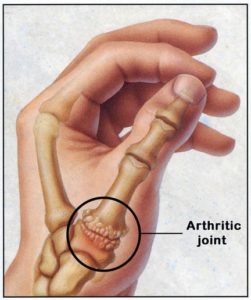
In a normal thumb joint, known as the carpo-metacarpal (Thumb CMCJ) joint, cartilage covers the ends of the bones acting as a cushion and allowing the bones to glide smoothly against each other. With thumb arthritis, the cartilage that covers the ends of the bones is lost. The bones then rub against each other, resulting in friction and joint damage.The damaged joint can produce noticeable lumps on the thumb joint.
Cause
- Aging
- Previous trauma or injury to the thumb joint.
- Certain hereditary conditions, such as joint ligament laxity and malformed joints.
- Medical Conditions – Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriasis.
- Activities and jobs that put high stress on the thumb joint.
Presentation
- Pain at the base of the thumb on griping, grasping, pinching or loading of the thumb.
- Swelling & stiffness at the base of thumb
- Reduced strength when pinching or grasping objects
- Reduced range of motion
- Enlarged or bony prominence of the joint at the base of your thumb
Treatment
Non surgical treatment can help in the early stages of the disease. This includes :-
- Activity Modification
- Painkiller – Non steroidal Anti-inflammatory Medications.
- Thumb Spica Splint
- Steroid Injection
Surgery
Surgery is advocated when the pain is intractable or on failure of non surgical treatment. Options include:
- Joint fusion (arthrodesis) – The bones in the affected joint are permanently fused. The fused joint can bear weight without pain, but has no flexibility.
- Trapeziectomy – The bone at the base of the thumb (trapezium) is removed. This a gold standard procedure and provides excellent results.
- Joint replacement (arthroplasty) – Trapezium is removed and replaced, this is at preliminary stages and results are good only in the pioneering institutions.
After surgery, a cast or splint is worn over the thumb for up to 6 weeks. Physiotherapy is started after removal of cast or splint to help regain the hand strength and movement.
Metacarpo-phalangeal joint Arthritis (Knuckle Joint)
The knuckle joints of the hand are called the metacarpophalangeal joints (MP joints). These joint are important for both power grip and pinch activities. The MP joints are often affected by arthritis either from routine wear and tear, injury or medical conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout or Psoriasis. This results in pain and loss of function of the hand.
Treatments
Medication (NSAIDS) are helpful in relieving pain and may also reduce worsening joint destruction.
Injection of a steroid in the joint also helps to control pain.
If the joint is completely destroyed, then joint replacement or joint fusion are effective surgical options. These joints can be replaced with a silicone implant or other material (metal, pyrocarbon). Joint replacement is very useful, especially for older or less active individuals. Fusion (making the joint solid) is an effective treatment of thumb MP arthritis.
Inter-phalangeal Joint Arthritis (IPJ)
The joints between the bones of the finger (phalanges) are known as Interphalageal joints (IPJ). Loss of cartilage cover over the ends of these bones result in arthritis of these joints. There are 2 interphalangeal joints in each finger except thumb which has one interphalangeal joint. These are called the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ) and the distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ).
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Arthritis (PIPJ)
This joint is the next joint from the knuckle in the fingers. Arthritis of this joint presents with similar symptoms as the MC joint arthritis.Treatment of arthritis in these joints is replacement of the joints with silastic/pyrocarbon/metal implants. This provides pain relief and movement. Another option is fusion of the joint which provides pain relief but motion at the joint is lost.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint Arthritis (DIPJ)
This joint is end joint of the fingers. Arthritis of this joint presents with similar symptoms as the MC joint or PIP joint arthritis. The movement in these joint is lesser than other finger joints. Treatment of arthritis in these joints is fusion of the joint which provides good pain relief.
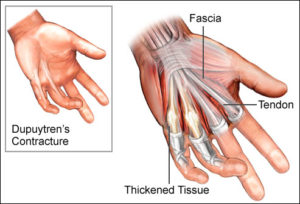
Dupuytren’s contracture is thickening of the palmar fascia resulting in contracture of the fingers. It typically appears after age 40 and grows more common with age. It more common in men than women and is often hereditary.
Younger age at presentation is associated with a severe disease condition. Initial presentation is with small nodules or indentations followed by development of thick cords that curl the affected fingers.
Treatment
Dupuytren’s disease requires surgical removal of the thickened, contracted tissue. Following surgery hand physiotherapy is required to regain strength and range of motion. A full recovery and return to activities can take 6 – 8 weeks.
Recent advance in treatment includes use of Xiaflex injection. Xiaflex is an enzyme made from the bacterium clostridium that dissolves collagen.
Treatment with Xiaflex is a clinic based procedure with injection directly given into the thickened tissue. Two days later, the patient require manipulation under local anaesthesia to straighten the fingers. Patients are required to wear a splint at night to hold the finger straight and prevent it from curling up again.
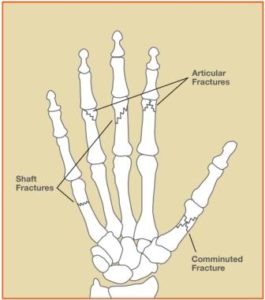
Thumb Fractures
- Bennett’s Fracture
Bennett’s fracture / trauma is an intra-articular fracture dislocation of the thumb metacarpal at the carpometacarpal joint. It is caused by a direct blow to the thumb in a partially flexed metacarpal. The thumb metacarpal is typically displaced radially and dorsally due to the pull of thumb extensors.
Treatment
If adequate reduction can be achieved, than the fracture / trauma can be treated non surgically in a thumb spica splint.
- Rolando Fracture.
This is a complex intra-articular fracture / trauma of the thumb. The fracture has a similar ulnar fragment as seen in Bennett’s fracture but also has a large dorsal fragment that gives the fracture lines a “Y” or “T” shape.
The Rolando fracture almost always requires surgery to obtain good anatomic alignment. The overall outcome depends on alignment of the fracture at the time of surgery and stability of surgical fixation.
This fracture / trauma typically requires surgery to ensure good alignment and reduction of the fracture as this reduces the risk of osteoarthritis and permanent disability.
Little Finger Fracture (Boxer’s Fracture)
This is the commonest fracture of hand and occurs through the neck of the fifth metacarpal, typically after punching a hard object. Patient presents with pain over the “knuckle” (distal metacarpal) and a palpable depression or loss of the normal “knuckle” contour. This fracture requires reduction and application of a plaster/splint.
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture / Trauma
These fractures can lead to significant long-term disability if not reduced and treated properly. It is important to ensure that there is no rotational deformity and that any significant angulation is reduced at the time of reduction.
Patients with displaced, angulated, comminuted, spiral, or oblique fractures of the metacarpal shafts should be treated by a hand surgeon. Oblique, spiral, comminuted fractures, fractures with significant angulation or rotation require surgical treatment.
Phalanx Fracture
Proximal and middle phalanx fractures are unstable and can result in significant angulation or rotational deformities. Formation of scar tissue around the tendons result in additional complications and a significant functional decline. These fractures often require dynamic splinting, finger splinting or surgery undertaken by expert hand surgeon.
Distal phalanx fractures can often be treated with an appropriate splint, except when there is an intra-articular component that requires surgical correction by a specialist hand surgeon.



