The wrist joint is the most complicated joint in the body. It is made of multiple bones and soft tissues (tendons, ligaments, and muscles) – to enable the hands to be both flexible and strong.
Injuries to the wrist present a significant clinical challenge, and are always advocated to be treated by a well trained specialist to obtain an early and complete functional recovery.
Dr Tawari is a fellowship trained Orthopedic Wrist & Hand surgeon in Mumbai, India. He undertook his fellowship in wrist & hand surgery at the Pulvertaft Hand Centre (UK) which is a pinnacle institute for wrist & hand surgery in the United Kingdom and the world.
Dr Tawari routinely undertakes simple and complex wrist fracture / trauma surgeries, wrist arthroscopy, wrist reconstruction operations to deliver unequivocal results and functional recovery to his patients.
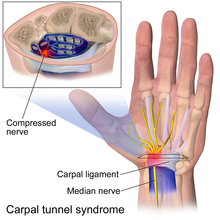
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a common, painful, progressive condition that is caused by compression of the nerve (median) at the wrist area.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include numbness and tingling sensation in all the fingers except little finger
Pain and burning sensation in hand and wrist that may radiate up the arm and elbow and weakness in hand with diminished grip strength.
Causes
Exact causes of the condition are not known. However factors often associated include congenital abnormalities, repetitive motion of hand and wrists, fractures and sprains, hormonal imbalance, and other medical conditions such as hypothyroidism, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, obesity, gout, overactive pituitary gland, or the presence of a cyst or tumor in the canal.
Treatment
Carpal tunnel syndrome treated based on the severity and duration of the symptoms.
The Non surgical treatment includes:
- Treating underlying medical conditions
- Hand and Wrist splint to be worn at night
- Activity Modification
- Physiotherapy - Strengthening and stretching exercise
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Steroid injections
Surgery
As it is a progressive condition, surgery is considered to prevent further damage to the nerve occurring due to on-going compression.
Surgery involves up to a 2- inch incision in the palm and wrist area, the transverse carpal ligament is dissected to release the pressure on the median nerve and enlarge the carpal tunnel. A newer endoscopic technique allows a small surgical scar and a shorter recovery duration.
Surgery has a very good success rate and over 95% of patients are satisfied. Post operative full recovery may take from 6 weeks to 3 months.
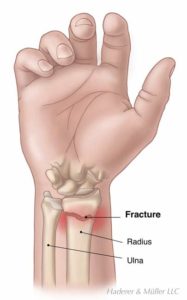
The wrist is comprised of two bones in the forearm, the radius and ulna, and eight tiny carpal bones in the palm. The bones meet to form multiple large and small joints. A wrist fracture / trauma refers to a break in one or more of these bones.
Types of wrist fracture / Trauma include:
- Simple wrist fractures – The fractured pieces of bone are well aligned and stable.
- Unstable fractures – The fragments of the broken bone are not aligned and displaced.
- Open (compound) wrist fractures are severe fractures in which the broken bones cut through the skin. This type of fracture require immediate medical attention.
Causes
Wrist fractures / trauma caused due to fall, vehicular accidents or workplace injuries. Sports such as football, cricket or kabaadi may also be a cause of wrist fractures. Wrist fractures / trauma are more common in elderly people with osteoporosis.
Presentation
Common symptoms of a wrist fracture include severe pain, swelling and limited movement of the hand and wrist. Other symptoms include:
- Deformed or crooked wrist
- Bruising
- Numbness
- Stiffness
Treatment
Fractures that are not displaced are generally treated with either a splint or a cast to hold the wrist in place.
If the wrist bones are displaced than surgery is often required. Devices such as rods, plates and screws are used to allow adequate alignment of fracture until healing. After surgery some motion exercises to keep your wrist flexible is encouraged. Hand Physiotherapy helps to improve function, strength and reduce stiffness.
The scaphoid is one of the eight small bones in the wrist. During wrist motion, the wrist bones move together to allow the wrist to achieve many positions that we take for granted. The scaphoid “directs” the motion of the other small bones.
The scaphoid generally breaks following a fall onto an outstretched hand. If the scaphoid is broken, the blood supply to the bone gets severed and it often takes a long time (a few months) to heal. A fracture that is healing more slowly than expected is a “delayed union” fracture. A scaphoid non-union fracture refers to a wrist fracture that is failing to heal.
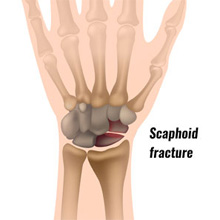
Presentation
Most patients with a scaphoid fracture will have pain and/or swelling along the thumb-side of the wrist.
Diagnosis is confirmed most commonly with x-rays. CT scan and/or MRI is required to gain knowledge on the shape and alignment of the scaphoid and assist with surgery (if required).
Treatment
Treatment without surgery can include use of a brace, anti-inflammatory medication or cortisone injections for pain relief, but this is temporary. Treatment of a scaphoid fracture/non-union requires surgery with or without bone grafting.
The aim of treatment is to relieve pain, maximize function and prevent arthritis. In delayed presentation or failed intervention, other surgical options include radial styloidectomy, proximal row carpectomy, scaphoid removal and limited wrist fusion, wrist arthroplasty or total wrist fusion.
Ganglion cysts are fluid-filled lumps that most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of wrists or hands. It looks like a water balloon on a stalk and contains a clear fluid or gelatinous material. Ganglion cysts are noncancerous, generally harmless and disappear without any treatment. However, if the cyst becomes painful or interferes with hand movement, they can be treated non-surgically or removed surgically.
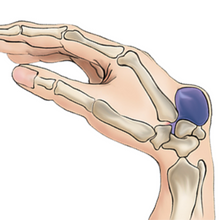
Causes
The underlying cause for ganglion cysts is not clearly known, but seems to develop when the synovial tissue bulges outwards. It is commonly seen in women and young people between 15 to 40 years of age. Osteoarthritis, tendon or joint injuries, and repeated stress applied to the wrist can lead to the formation of the cysts.
Symptoms
Ganglion cysts manifest as a visible bump under the skin. They may or may not be painful. If a cyst presses on a nerve it can cause pain, muscle weakness and a tingling sensation.
Treatment
Ganglion cysts can disappear without any treatment. Though aspiration can be suggested it is often unsuccessful as the fluid is thick & gelatinous often averted to aspiration.
Surgery
If the cyst continues to be painful, limits activity, causes numbness or tingling of the hand or fingers, then surgery to remove the ganglion cyst is recommended.
Surgery can be open or with arthroscopy, and the outcome is very good. There is a small recurrence rate of 10% associated with wrist ganglion.

